SPF DKIM DMARC explained
What even is SPF, DKIM and DMARC?
SPF, DKIM and DMARC are simply a set of email authentication protocols, that prove to ISPs and mail services that senders are truly authorized to send email from a particular domain. These tools provide proof that an email message is genuine and that it’s coming from who it claims to be from.
SPF
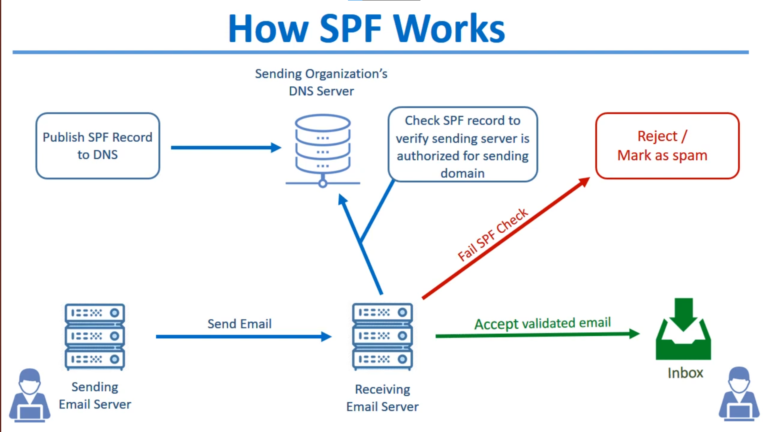
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a DNS record containing information about servers allowed to send emails from a specific domain (for example, thetechcorner.org). To do that, the domain owner can add a file or record on the server which tells the receiving server what domains are actually allowed to send emails.
SPF is both useful for protecting against “MailFrom” spoofing of your domain towards your users, but also to external destinations where it could harm your brand. Ie, Microsoft’s SPF record stops “MailFrom” spoofing from @microsoft.com not just to @microsoft.com but also to you which helps stop some fake Microsoft phishing emails.
1
2
#How does it look like
v=spf1 include:5123454.thetechcorner.org ~all
DKIM
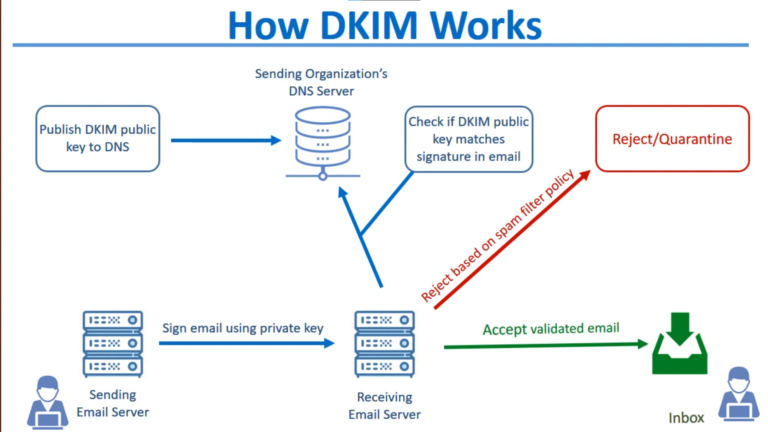
DKIM or (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an authentication similar to SPF. DKIM is a key-pair signing mechanism for the header of mail messages. . When you send mail you attach a signature to the message using a private key which is compared to a public key published in DNS for your domain. DKIM adds authenticity to a message and guards against tampering with the header by down-stream mail servers. One of the benefits to working on the header is it survives SMTP relaying and auto-forwarding.
DKIM is added as a TXT record by adding it to your domain panel.
DKIM does not directly prevent abusive/malicious behavior. DKIM is just a signature… If I hand you a letter with my signature on it there’s added authenticity; However, if I hand you a letter without my signature if there’s no requirement for the letter to be signed there’s no reason to be suspicious. It’s like SSL, just because a website doesn’t have SSL doesn’t mean it’s fake, but it’s preferred when SSL is used.
1
2
#How does it look like
k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCksjlkdixcieJDDSFIELDSKfdsfsdfsdfsfksflsfldfsfjhsdfsdfhuisdhfuiehfhNyyHs77EoDFDDEEFFEKJKLJHLKifLN51IIvwIDAQABQp6nIyi5oioyZh+1jDXoCDDFDSFEEDSFSEFE85N7b76aTtHmy2wTgR2LFS
DMARC
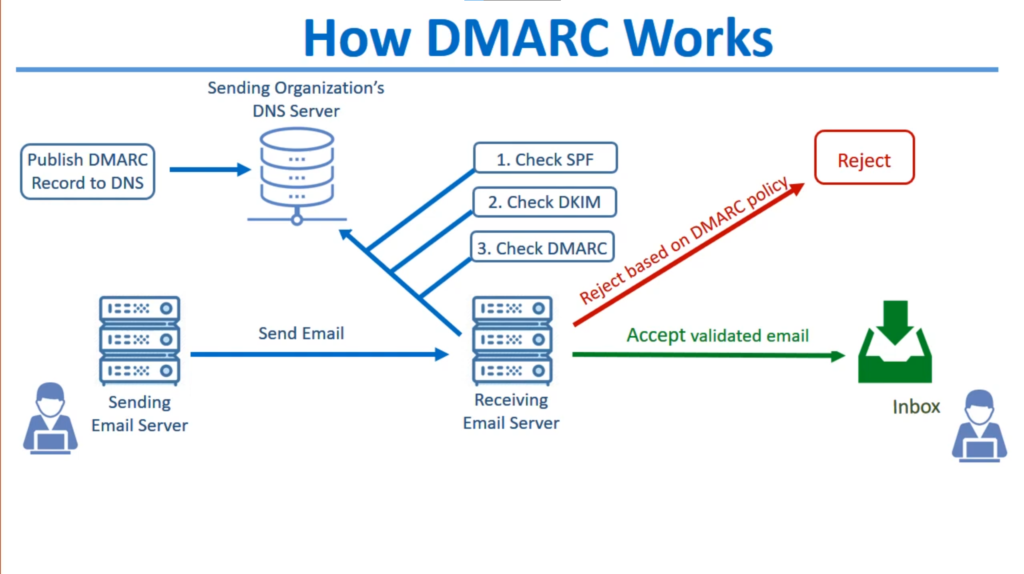
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) defines how the recipient’s mail server should process incoming emails if they don’t pass the authentication check (either SPF, DKIM, or both).
If the message fails authentication, it’s processed according to the selected DMARC policy: none, reject, or quarantine.
- Under the “none” policy, the receiving server doesn’t take any action if your emails fail authentication. It doesn’t impact your “deliverability”. But it also doesn’t protect you from scammers, so we don’t recommend setting it. Only by introducing stricter policies can you block them in the very beginning and let the world know you care about your customers and brand.
- Here, messages that come from your domain but don’t pass the DMARC check go to “quarantine.” In such a case, the provider is advised to send your email to the spam folder.
- Under the “reject” policy, the receiving server rejects all messages that don’t pass email authentication. This means such emails won’t reach an addressee and will result in a bounce.
The R in DMARC is for the Reporting component of the protocol. These reports allow the domain owner to see where all email using their domain in the From address is being sent from.
The DMARC record of the domain in the header from the address is used if it exists. Like the above records, it exists as a TXT record in DNS.
DMARC conformance check is called “alignment” and it checks that the header from is “aligned” with other authenticated domains on the message, either via DKIM or SPF. If either DKIM or SPF alignment passes, DMARC evaluates as a “PASS.”
SPF Alignment: The domain in the header from and envelope from must be the same (or sub-domains of the same parent domain if “relaxed”) and must pass SPF.
DKIM Alignment: DMARC requires a valid signature where the domain specified in the d= tag aligns with the sender’s domain from the header from the field.
1
2
#How does it look like
_dmarc.thetechcorner.org. IN TXT "v=DMARC1\; p=none\; rua=mailto:dmarc-aggregate@65.108.148.51\; ruf=mailto:dmarc-afrf@65.108.148.51\; pct=100"
TLDR:
- Envelope from spoofing: SPF
- Header from spoofing: SPF + DMARC, DKIM + DMARC, or SPF + DKIM + DMARC. No one mechanism alone will be sufficient.
- Display name spoofing: Advanced threat filters, transport rules, and user training. None of the mechanisms care about the display name.
- Compromised mailboxes or “legitimate” senders: Advanced threat filters, transport rules, and user training.
Useful tools:
Multiple mail tools like SPF lookup, blacklist DMARC MX toolbox
SPF, DKIM DMARC training tool Learn DMARC
Validate your SPF record Kitterman
Check your mail server/domain score Mail Genius